
The most common cause of back pain is the development of musculoskeletal diseases (such as osteochondrosis). If this pathology is mainly found in the elderly and is less common in middle age, then osteochondrosis has become much younger now and can usually be diagnosed in people between 20 and 30 years old.
According to medical statistics, the disease most often involves the lumbar spine and lumbar ral spine.
Disease characteristics
Osteochondrosis is a pathology that affects the musculoskeletal system of the spine, the most important component. It is caused by the fact that dystrophic changes of the intervertebral disc begin to develop.
The disease not only affects the tissue of the intervertebral disc, but also the surrounding tissues begin to show negative changes, affecting ligaments and muscles.
The cause of the epidemic of lumbar osteochondrosis is the maximum physiological pressure on this specific part of the spine.
For this disease, the characteristic changes occur in the nucleus pulposus (part of the intervertebral disc). The CD performs an amortization function.
If the water exchange in the intervertebral discs is disturbed, they will become thinner and their brittleness will increase.
Older people are most susceptible to pathological processes, because the metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc tissue begin to deteriorate when they reach a certain age.
Under the influence of negative changes, the boundary of the nucleus pulposus gradually expands and tends to enter the intervertebral space. This usually ends with the displacement of the nucleus to the spinal canal, the result of which is compression and compression of nerve fibers and blood vessels.
Pinched nerve is the cause of osteochondrosis pain. The function of internal organs may also deteriorate.
With the development of pathology, the pressure on the vertebrae increases. The body tries to compensate for this defect, and the growth of the bone tissue of the spine is significantly accelerated. As a result, pathological growth-osteophytes are formed on the vertebrae. Ultimately, this further disrupts the function of the affected spine.
With the development of osteochondrosis, patients may experience paralysis of the lower limbs. A person may become disabled due to lack of timely access to medical services.
Causes of lumbar and lumbar osteochondrosis
The occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine and lumbar ac spine is caused by improper load distribution of the spine. If other unfavorable factors are added, the progress of osteochondrosis will accelerate, and it may become more serious.

Diseases can be caused by:
- Regularly perform heavy physical labor and lift heavy objects (people in certain professions and athletes involved in weightlifting are dangerous);
- Insufficient physical activity will have a negative impact on muscle condition, and cause deterioration of blood circulation, reduction of metabolic processes and nutrients entering the tissues;
- The fact that the patient is overweight, causing the spine to continue to bear a heavy load;
- Problems with posture and gait discomfort;
- Congenital malformations or the presence of other defects in the spine or the entire bone;
- Flat feet may also lead to the development of osteochondrosis, because in patients with foot deformities, the arch of the foot cannot fully absorb the load during exercise, resulting in increased load on the intervertebral disc.
- Spinal trauma;
- Genetically determined bone tissue formation diseases;
- Age-related changes;
- Infections affecting bone tissue (tuberculosis, osteomyelitis);
- Inflammation processes affecting bones and joints (including rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis);
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- Contact with harmful and toxic substances.
The most common cause of pathology is the heavy burden on the spine of patients with incorrect posture.
Disease symptoms
The manifestation and severity of osteochondrosis symptoms depend on the stage of the disease.

The disease is divided into 4 stages:
- In the second stage, the annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc is destroyed. The vertebrae become unstable, their mobility increases, and the result is a stable tension of adjacent muscles. Pain along the sciatic nerve. At this stage of the disease, sometimes it starts to destroy the work of internal organs.
- In the third stage, rupture of the annulus fibrosus and release of nucleus pulposus content were observed. As a result, a herniated disc is formed. All these lead to further deformation of the spine (the development of scoliosis, kyphosis or lordosis can be observed). Acute pain is permanent and is caused by radiation syndrome, in which nerve roots are compressed by fragments that fall outside the annulus.
- The fourth stage is characterized by severe spinal deformity and pathological growth of vertebrae. It may significantly relieve pain, but this does not mean that the patient's condition will improve. On the contrary, one's movements are severely restricted. Generally, patients with stage 4 osteochondrosis are required to register for disability.
- Low back pain-Acute pain attacks that start when you move suddenly or lift heavy objects.
- Lumbodynia-Frequent severe pain related to the damage of intervertebral cartilage and muscle fibers.
- Waist and hip pain-It is characterized by pain, chills or heat in the waist and legs.

A person’s mental state can also cause pain.
In addition to pain, osteochondrosis is also characterized by:
- The lower body and legs feel weak;
- Deterioration of tendon reflexes in lower limbs;
- Tingling, which can be felt from the lower back to the feet; Curvature of the spine;
- Skin problems (dryness, flaking, light blue tint) and changes in sweating can also occur in the lower back and buttocks.
If you notice the symptoms listed, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible so that treatment can be started quickly and serious consequences can be prevented.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of lumbar and lumbar spine
Medical
For patients diagnosed with osteochondrosis, doctors can prescribe the following types of treatments (including one treatment):
- medication;
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- Medical massage and manual therapy;
- Undergo surgery.

Let us take a closer look at these methods.
Prescription drugs can relieve pain, fight inflammation and improve the regeneration of diseased tissues. Can be assigned to patients:
- Analgesics (helps relieve pain);
- Muscle relaxants (used to relax muscle fibers and relieve cramps);
- Cartilage protector (promote the regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue and protect them from negative effects);
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- If edema occurs, diuretics (diuretics) should be used;
- Drugs that improve blood circulation;
- Vitamin and mineral complex.
For common forms of osteochondrosis, when conventional analgesics are ineffective, blockade medications can be prescribed. The doctor should consider the stage of the disease and the severity of the symptoms, determine which specific drug should be used, and the treatment plan and duration.
It is recommended to prescribe physical therapy together with drugs to improve the therapeutic effect. For osteochondrosis, the following operations are required:
- Laser therapy;
- Magnetic resonance therapy;
- Make a voice;
- Shockwave therapy.
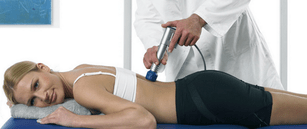
These therapies help relieve pain, reduce inflammation and repair damaged tissue. The use of laser beams is very effective, which allows you to obtain stable reflections.
When vocal therapy is prescribed, other topical medications should be used (this method allows the medication to penetrate deep into the skin and directly into the lesion). In order to maximize the use of oxygen-enriched tissue, doctors may also prescribe ozone therapy.
It should be remembered that physical therapy is contraindicated in certain pathologies. For patients suffering from tumor diseases, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, tuberculosis, infectious diseases, no prescription should be given.
Massage and manual therapies can be prescribed at the same time as medications and physical therapy procedures to improve the therapeutic effect.
These methods affect the transmission of nerve impulses and help normalize muscle tone.
Only when other treatments for the disease are ineffective, surgical intervention is performed in the late stage of the disease. If the following conditions are met, surgery is required:
- The patient suffers from severe pain that cannot be controlled by medication;
- Intervertebral disc herniation;
- was diagnosed with spinal cord compression (which can lead to impaired sensitivity and motor function-paralyzed from weakness);
- noticed the development of cauda equina syndrome.
Nowadays, modern high-tech and low-traumatic surgery are performed more and more frequently, which greatly shortens the recovery time. In the absence of complications, the patient will be able to move normally within a few months after surgery.
Folk remedies
Traditional medical therapies help relieve pain, reduce inflammation and improve mobility. These are several ways to treat osteochondrosis through folk remedies.
- You need to pick up raw potatoes, grind them, and mix them with natural honey. The resulting mixture should be placed on your back and bandaged for at least 2 hours. Spreading hot boiled potatoes on the affected area also helps.
- Grate garlic and mix with equal parts ginger. Then add some olive oil. The medicine must be rubbed to the back at night to improve blood circulation and reduce muscle tension.
- Mix a spoonful of peppermint oil with a spoonful of fir oil. The mixture should be rubbed onto the back.
- Chopped pine or spruce needles at ½ tablespoon per 200 ml (1 cup) of boiling water, cook for 30 minutes. Drink ½ cup 2 times a day.
- Mix a tablespoon of bilberry and peppermint herb, add boiling water (1 cup) to boil, brew and strain. Gradually drink the broth throughout the day.
It is important to understand that treatment with folk remedies is not a substitute for visiting a doctor. Folk methods can temporarily relieve symptoms, but they cannot completely eliminate the disease.
In addition, they may not be suitable for all patients, so it is strongly recommended to consult an expert before use.
Physiotherapy practice
Physical therapy exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles of the lower back, buttocks and thighs, which help relieve pain, reduce nerve and blood vessel contraction, and restore flexibility.
To make the exercise as effective as possible without causing harm, certain guidelines must be followed:

- You should exercise in natural fabric clothing that does not restrict exercise;
- The lumbar spine should not be cold during sports.
- If you need to exercise in a prone position, it is best to put a round roller under your calf;
- You should start exercising within one hour after eating;
- In order to obtain sustainable positive results, it is necessary to practice physical therapy regularly;
- Exercise should be done smoothly and slowly, and focus on muscle work;
- You need to monitor your breathing, which should be even and deep.
- It is helpful to keep a diary with changes from the day you start the practice.
Which exercises should be performed depends on the severity of the symptoms of osteochondrosis.
In acute lumbar osteochondrosis, the spine should not be loaded, bed rest should be insisted (preferably using an orthopedic mattress), and physical exercise can be carried out while lying on the back. Repeat 8-10 times each time. Here are some suggestions:
- Lie on your back, put a roller under your calf and bend your knees. The patient should bend the arm into a fist and straighten it, and also need to bend the leg at the ankle. Each arm and leg performs these movements alternately.
- You need to bend and relax your legs alternately, moving only your knees. At the same time, the back should not move.
- Rotate each foot in turn.
- Stretch your arms and legs, then start bending and stretching the elbows of your arms at the same time. During flexion, you need to inhale, and during stretching, you need to exhale. Keep your palms up.
It is recommended to practice subacute lumbar osteochondrosis:
- Bend your knees into a supine position and place your feet on the mattress. When inhaling, gently lift the bone, and the lower part of the thoracic spine should be placed on the mattress. After 1-2 seconds, gently lower the lower part of the back.
- Lying on the bed while breathing in, you need to raise your head and tighten your abdominal muscles. When exhaling, return to the starting position.
- In the supine position, slide your heels to your hips without lifting them from the mattress. After a few seconds, straighten your legs. The action should be repeated for each leg and both legs at the same time.
- Sit up from all fours, place your hips on your heels, and slide your hands on the mattress. Then take the starting position.
- Relax your limbs and relax your neck. Tighten your chin to your chest, bend your lower back like a cat, and fix it for a few seconds. It must be ensured that the head does not lift and the back maintains its acceptable position.
Patients who have achieved remission can do any of the above exercises.
If possible, for any form of lumbar osteochondrosis, physical therapy exercises should be performed 3-4 times a day, but you should definitely consult a doctor before starting physical therapy.
Preventive measures
Like most other diseases,osteochondrosis is much easier than trying to eliminate its consequences later. In order to minimize the chance of suffering from this disease, it is recommended:
- to ensure a healthy and balanced diet.
- Live an active life and act as much as possible;
- Don’t put too much load on the spine;
- Do some exercises to strengthen your back muscles.
It is also necessary to promptly treat diseases and injuries that may lead to the development of osteochondrosis. If even mild symptoms may indicate a spine problem, you should not delay seeing a doctor.
Conclusion
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a disease that must be taken seriously to avoid serious consequences. If you stick to a healthy lifestyle and follow the recommended precautions, you will be less likely to get sick.
If you do experience symptoms of illness, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Timely medical care is the key to stable remission. It allows you to stop the pathological process, maintain the patient's ability to work, and restore the previous state of the musculoskeletal system to a certain extent.






















