Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a chronic, slowly progressive lesion of the vertebrae of the cervical spine (from the first to the seventh), which begins with the destruction of the intervertebral discs and ends with their "subsidence", protruding (hernia), a change in the shape and displacement of the vertebrae (degenerative-dystrophic process).
Subsequently, the nervous system (compression, inflammation of the nerves and its consequences) and vascular complications (compression of the vertebral artery and the consequences of blood circulation disorders) connect the clinical symptoms of osteochondral bone marrow disease. For cervical osteochondrosis, these are headaches, dizziness, loss of direction, nausea, sharp drop in stress, and difficult to normalize. Osteochondrosis is a common pathology, and symptoms occur in 90% of people (regardless of gender) by the age of 45, in front of others - for office staff who are doing with a sedentary lifestyle. The lesions in the cervical area were diagnosed with lumbar osteochondral disease. This is due to excessive weaknesses in the neck and muscles around the spine in this area.
The nature of pathology that follows
The intervertebral disc (abbreviated MPD) is the central water slurry core, surrounding its elastic, strongest fiber shell. The adjacent vertebrae is adjacent to it and below. As diffusion (direct and reverse filtration, molecules penetrate into the disc and the back) from the bone tissue of the vertebrae, the reception (and excrement) of substances and water into the discs is caused by diffusion. The gradual aging of the intervertebral disc fabric leads to the fact that the receipt of the required substance is slowed down and, under the influence of an outrageous factor (pressure, load), it ceases completely. The dense fabric of the fiber membrane is covered with cracks, losing its elasticity, and the core of the pulp in the center will dry (lost water). This leads to the fact that cervical osteochondrosis progresses:
- MPD loses height;
- The body of the vertebrae moves, the nerve roots are squeezed, and start growing with bone spikes, trying to evenly disperse the increase in pressure (spondylosis).
Over time, ligaments are involved in the ossification process, which impregnate calcium at the location where the vertebrae attaches, and become the cause of stiffness, which is the constraint of the neck. As people continue to load their spine - they are actively moving, they sit in an uncomfortable position:
- The body of adjacent vertebrae is increasingly compressed by MPD.
- This leads to the fact that the slurry nucleus (rather than the rest) is pushed forward or backward (more often in the anterior longitudinal ligament because it is thin in the cervical area).
Such a herniation is called a herniation (the shell of the disc has not exploded, but has only changed its shape), and it presses against adjacent tissue, which causes muscle tension, pain and other obvious occurrences of cervical bone cartilage. Over time, the fibrous shell of the disc is torn and part of the striatal nucleus is squeezed into the fabric (this breakthrough is called hernia). At this stage (this is 4 stages), all acute symptoms of the disease can disappear (a small portion of the nucleus is absorbed by calcium or is covered with calcium and stopped to stimulate surrounding tissue), or, on the contrary, leads to the development of ischemic stroke in the cerebral (oxygen starvation, death in the hungry area) and instability.
Causing factors
Considering the reasons for osteochondral toxin, it is worth noting that the basis of the violation is the natural aging of the intervertebral disc fabric. This process can speed up different triggers:
- Genetic tendency.
- Congenital defects develop in the cervical spine (deformation of the body of the first cervical spine).
- Impairment and surgical interventions.
- Excessive mobility in the cervical area (e. g. , during exercise training).
- Lack of physical exercise (sitting work).
- Violate posture (bend).
- age.
- Neurological pressure.
- Low temperature.
Four stages (degree) and symptoms
With osteocartilage degeneration in the cervical vertebrae, all manifestations intensify from stage to stage. The more changes occur in the vertebrae disc, the stronger the symptoms of osteocartilage bone marrow. In a person's initial stages, muscle tension on the neck and shoulders may be disturbed because they quickly become tired. Then the main signs of pathology appear - the head, shoulders, arms, chest, pain that can be masked for tooth pain. A person begins to be dizzy, with less concentration and less eyesight and hearing, which can worsen the quality of life and will not affect his ability to work. Gradually, symptoms increase and increase - a person will wake up from stiffness in the spine, and during a period of intensification, any sharp movement (e. g. , sneezing or heels on the floor) can cause pain in the cutting of the neck and affected nerves, which becomes difficult to lift the finger or hold the object of the finger. At night, the heartbeat may be exacerbated, or the lack of air may cause concerns - due to the pain, the patient cannot breathe deeply, a person cannot move, turn his neck or raise his hand. Among the symptoms, osteochondrosis in men is almost no different from osteochondrosis in women (they often worry about headaches.
Stage 1 (degree)
The disc loses elasticity and sags.
At this stage, osteochondrosis occurs in the neck area, with tension, fatigue, muscle fatigue and neck pain occurring.
The first symptom:
- Muscle tone, which leads to rapid fatigue and fatigue;
- Pain, neck discomfort;
- Headache occurs regularly.
Stage 2
MPD cracks, exfoliating, sagging more, protrude into (protrusions of the fibrous membrane), and bone growth occurs at the edge of the vertebrae.
- A person's tightness, headaches, sensitivity disorders, pain in the neck can aggravate the basic load, thus bringing it to other parts of the body.
- The pain sensation in the neck, chest and occipital bones is enhanced by load.
- The person is often worried about severe headaches.
- Crystal when turning your neck.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Blood pressure stimulation.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness of the skin and fingers, weakening of the muscles of the limbs.
Stage 3
At this stage, protrusions erupt (hernia), the size of the bone spike increases, and the spinal ligament is ossified at the attachment position of the vertebral body. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are in 3 stages:

- The first two stages of the disease are symptomatic with invasion of the blood supply to the brain (due to compression of the vertebral artery), in the form of visual defects, hearing, orientation, sensitivity, etc.
- The pain will shoot in the ears, chin, shoulders and forearms with the maximum movement of the most basic movement (tilting the head).
- The patient is looking for a convenient position to try to find a head tilt that can relieve symptoms.
- His attention was distracted, and the coordination of memory, vision, hearing, and movement was deteriorating, sleep disorders, nausea, and stable hypertension.
- Significant stiffness, relief, tetraplegia (fixility, impaired sensitivity), muscle loss of strength and volume (atrophy).
- Smooth curves of the spine were observed.
Stage 4
A feature of the fourth stage - cervical osteochondrosis symptoms are weakened and stiff.
- As soft tissue is ossified (ossification), the acute manifestations of the disease gradually fade.
- In 5% of cases, necrosis in adjacent tissue is a brain ischemic stroke that may complicate the 4 stages of osteochondrosis.
- The manifestations cause ischemic stroke (oxygen starvation and withering cells) and disability.
Possible complications of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Ischemic stroke in the brain may lead to disability in the patient;
- Patients may suffer from nutritional ulcers (cell death due to lack of nutrients and oxygen).
Diagnostic method
Osteochondrosis in the cervical area was diagnosed using various instruments:
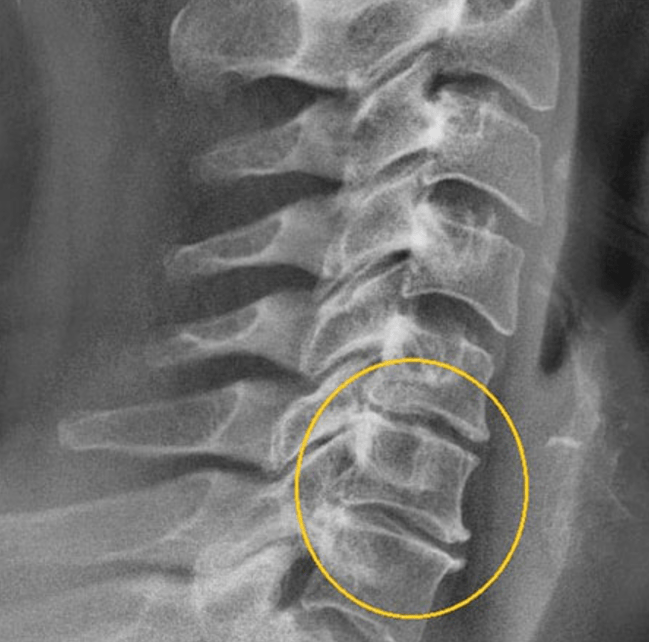
- x -ray (characteristic diagnostic features or reduction of MPD height along the edge of the vertebrae occurs in 2 stages).
- CT, MRI of the spine (allowing you to diagnose changes in MPD in the initial stage).
- Records (research with the introduction of contrast agents can allow you to establish the deepest damage to the disc).
- Electronics (with its help determines the barrier, inflammation of the nerve end).
- Multiple placement of blood vessels in the cerebral (allows you to determine the condition of the blood vessels and blood flow).
If the nerve ends are impaired, many neurological manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis occur, detect symptoms and monitor treatment by a neurologist (helps to establish a diagnosis, suggest, prescribe medication).
Treatment method
Osteocartilage in the neck is an incurable disease (such as any other localized osteochondria), changes occurring in the tissues of the intervertebral disc, irreversible. In early stages (1 and 2), it can be paused with conservative treatment, and at stage 3, conservative treatment is prescribed to relieve acute symptoms. Sometimes, stable cervical radiation inflammation (inflammation of the spinal core of the spinal nerve) is performed, and the intervertebral disc is surgically removed.
first aid
If the patient feels acute pain in the neck, is unable to turn his head, and is unable to make any other movements (raising his hand), first aid for cervical osteochondrosis is required. In this case, 2% anesthetic or other drug solution with combined properties is introduced into the muscle along the vertebrae. The lockdown quickly relieves pain and improves the patient's condition. The blood circulation of cervical spine and neck mobility can be improved through warming agents, and osteocartilage degeneration of the cervical spine is treated.
Other treatments:
Experts can recommend various orthopedic equipment:
- Shantsz's tires are a corset, bandage or neck fixator. With its help, the head is secured in one position, which relaxes the muscles, unloads and anesthesizes the cervical spine.
- An orthopedic pillow that allows you to fall asleep in the most convenient and physiological position without causing muscle tension, pain and stiffness in your spine.
Surgery
if:
- Vertebral hernia (or hernia) increasingly compresses nerve roots.
- Other treatments will not alleviate the patient's condition;
- There is a threat of disability.
Surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can significantly improve the patient's condition, but there is always a possibility of developing various complications (loss sensitivity, spinal mobility).
Family therapy
Home treatment for osteochondrosis is a product that can help:
- Strengthen blood circulation in the tissue.
- Improve their metabolism.
- Finally get rid of pain, inflammation and muscle tone.
When acute symptoms of the disease are abandoned, they are used during recovery:
- Heat and compress with Campal alcohol. Take 50 ml of vodka, campusal alcohol, fresh aloe juice, 50 grams mustard powder and 100 ml of honey. Mix, add 3 fresh egg egg egg whites to the mixture and stay for a day. By ready, apply the mixture to the affected area along the ridge (lasting 2-3 hours) covered with plastic film. The treatment process is 12 procedures and can be repeated in one week.
- Ginger ointment. Grind 3 medium garlic teeth and 50g fresh ginger root in a blender, add 50g butter at room temperature and stir again. Using this tool, apply the damaged area once a day (for 2-3 hours) and is covered with a membrane. The treatment process for cervical osteochondrosis is 21 days and can be repeated after 2 weeks of rest.
Any non-traditional treatment should be discussed first with the subject doctor.
prevention
Measures to prevent bone cartilage are:
- Moderate physical exercise and neck exercise;
- A diet rich in vitamins, which can be used for cartilage;
- orthopedic pillows and mattresses to sleep;
- Convenient workplace.
You need to be careful to carry heavy habits in one hand, or to get rid of it with a bag on one shoulder. Such loading is a provocative factor in the development of cervical osteochondrosis.
forecast
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common pathology in 90% of people (regardless of gender) after 45 years of development. More often diagnosed:
- cervical or cervical sternum (due to weaknesses in the cervical muscles and neck mobility);
- Lumbar osteochondrosis (due to the load on this spine);
- Less common - chest (the department has less mobility and very little load).
Violations of the disease are irreversible and therefore cannot cure the pathology. Conservative methods can be suspended by cervical osteochondrosis at stages 1 and 2. It will take 2 to 3 weeks to get rid of acute symptoms until osteochondrosis is fully restored. In stages 3 and 4, the most effective method is surgical correction (removal of hernia and discs, strengthening of vertebrae). Thirty years later, the prerequisite for all is the regular performance of special cervical movements, as this measure solves the problem of disease progression.






















