
Back pain is a common problem in middle-aged and elderly patients. This may be caused by lifestyle errors, musculoskeletal system diseases, and visceral diseases. Neurologists, orthopedics, nephrologists and urologists can treat back pain based on its origin. It is difficult for patients to find out the cause of the discomfort and choose the right doctor by themselves. Therefore, it is necessary to contact the therapist at first, and based on the symptoms, medical history, and the results of the research conducted, the therapist will refer you to a narrow specialist.
classification
Back pain can be:
- Myofascial.
- Hurt.
- Neurosis.
- Psychic cause.
Myofascial painObserved during the so-called formation process. Acupuncture points that trigger back muscles. The trigger point is a pea-like knot that forms when muscles continue to tense (when they cannot relax at all). Moreover, when a part of the muscle fiber is compressed, the other part is stretched. This affects the mobility of muscle fibers: it is limited. The fiber itself will shorten and become tighter.
The trigger point is due to excessive muscle tension. Moreover, excessive fatigue may occur not only due to excessive physical activity, but also due to staying in one position for a long time (for example, sitting on a computer). Similarly, osteochondrosis often triggers trigger points.
Another factor that contributes to the formation of trigger points is overstimulation of sarcoma (the basic contraction unit of protein complexes). If the sarcoma is over-stimulated, they will remain in a contracted state.
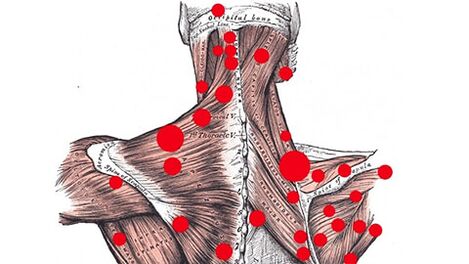
The presence of trigger points cannot relax the muscles completely. Even under a small load, she began to fatigue quickly, excessively exercised while moving, and recovered very slowly. Its limited range of motion affects the entire fascia chain. The mobility of other muscles, and even certain joints, also deteriorates.
The blood flow in the tissues around the trigger point is also affected. Therefore, hypoxia is observed in this area. The accumulation of decay products stimulates the trigger point and causes pain. In this case, the size of the muscle is not important, it depends entirely on the degree of stimulation of the acupuncture points. Even if there are trigger points, the smallest muscles can produce many unpleasant sensations.
A feature of myofascial pain is reflexes. This means that the pain is reflected to other parts of the body. They may occur in areas far away from the trigger point. Therefore, for example, due to the presence of nodules in the abdominal muscles, it may cause pain below the shoulder blade or lower back. Similarly, the lower back may be injured due to trigger points in the calf area or hips.
Myofascial pain is usually persistent and boring. Sometimes they only appear when moving, and sometimes when they are stationary. Their strength may vary: from mild discomfort to unbearable pain.
Nociceptive pain-The body's response to direct stimulation of pain receptors (nociceptors). In the case of the back, these are the receptors located in the paravertebral ligaments, muscles, tendons, and the joint capsule of the intervertebral joints and the outer third of the annulus of the intervertebral disc. Patients may experience pain due to reflex muscle spasms in the facet joints, malnutrition, or pathological processes. The pain worsens when moving.
Neuropathic painDevelop in the pathological process of the nervous system: damage the nerves or roots of the peripheral nervous system and destroy the central nervous system. This pain can be observed in osteoporosis, spondylolisthesis, hernias and spinal fractures. They are aggravated when bending, moving, straining, coughing, or sneezing, and in most cases, they are applied to the limbs. Sometimes they are dull and painful, but more often they are sharp and shooting.
Psychogenic painIt occurs due to muscle cramps caused by emotional stress, chronic stress, or anxiety.
In some cases, varieties can be combined with each other. For example, myofascial sensation and nociception coexist.
In addition, back pain is divided into 3 types:
- Acute (lasting less than 6 weeks).
- Subacute (6-12 weeks).
- Chronic (more than 3 months).
Acute/subacute painIt usually develops due to wounds, wounds, tissue damage (deep, superficial) caused by inflammation. Therefore, the body warns us that something is wrong. After the tissue is completely healed, the pain disappears.
Chronic painOccurrence is due to organ and system diseases or mood disorders. If it exists, a comprehensive medical examination must be performed.
By location, the pain may be:
- Local.
- Reflect it.
- radiation.
Local pain develops directly at the site where the pathological process develops. Reflect-if there is a trigger point. Radiation-damages internal organs and spreads along nerve fibers.
Why does my back hurt?
Back pain can be caused by a variety of reasons, including:
- Spine curvature: scoliosis, kyphosis.
- Nervous system diseases: herniated disc, osteochondrosis, spondylopathy, spondylopathy.
- Endocrine pathology: osteoporosis.
- Respiratory diseases: pleurisy.
- Pathology of the kidneys and urinary system: urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis.
- Tumor.
Short-term pain (usually severe, burning) may be caused by a variety of reasons. These include:
- Injured
- Muscle overwork (due to monotonous posture or the performance of the same type of repetitive movement).
- Low temperature.
Pain caused by the degenerative process occurs in the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Intervertebral hernia.
- Herniated disc.
- Deformable spondylosis.
- Degenerative scoliosis.
- joint.
- Spondylolisthesis (displacement of the vertebrae).
- Spondylolisthesis (nonunion of pedicle).
- Spinal stenosis.
Pain radiated to the spine may be caused by the following diseases:
- Heart and great blood vessels: myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, aortic aneurysm.
- Lung: cancerous tumor, pleurisy.
- esophagus.
- Gallbladder and biliary tract: acute and chronic cholecystitis.
- Kidneys and urinary tract.
- pancreas.
In rare cases, back pain may be the source of infection. For example, sometimes my back is injured by the flu. Moreover, the infection may penetrate into the spine from nearby organs (urinary tract, kidneys).
Other causes of back pain may be changes in hormonal levels (for example, related to age, during or after menopause). In this case, hormonal spondylosis (degeneration of the spine) occurs
A lot of back pain: what to do?
If you feel severe pain, be sure to see a doctor as soon as possible. However, if the feeling is so strong that any exercise will cause torture, first aid is needed. You need to lie on your back on a flat, hard surface (such as the floor). This will help relieve cramps, relax muscles and relieve pain.
Sink on a flat surface, do not change the position of your back. Lie on your back and try to turn over. This can relieve the spine. When the pain subsides, step back. It is recommended to put something under your feet and lift them up. Lie in this position for 10-15 minutes.
You also need to climb correctly: first turn over. Start from this position. Then lean on something (if there is no support nearby, climb up) and slowly stand up. Only in this way can you carefully straighten your back.
To find out the cause of a serious back injury, please do not postpone going to the doctor. This will help avoid new attacks.
Diagnostic procedure
If you have back pain, you should definitely make an appointment with the therapist:
- Occurs during physical exercise and muscle tension;
- Lasts more than 3 days;
- Repeat popularly.
It is necessary to seek medical attention immediately in the following cases:
- Continuous injury to the back;
- Increased body temperature, numbness of the limbs, morning sleepiness of the limbs exacerbated the pain
- Pain will not disappear when lying on your back;
- The pain is worse at night.
At the appointment, the doctor will collect memories and examine the patient (evaluate skin condition, body position and symmetry, gait, etc. ). Then he will assign research:
- General analysis of blood and urine;
- X-ray
- CT examination;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
If necessary, the therapist will refer the patient to a neurologist, orthopedic doctor, urologist, gynecologist or nephrologist.
Back pain treatment
Back pain treatment is comprehensive and may include:
- Take medicines (anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers, restorative drugs);
- Blockade (long-term pain relief);
- Physiotherapy procedures;
- Physical therapy exercises;
- massage;
- Manual therapy.
If conservative methods cannot achieve the desired results, surgical treatment is required. Modern methods can perform precision surgery with low trauma in a short recovery time.
Prevent low back pain
Simple preventive measures can help prevent back pain. necessary:
- Monitor your posture.
- Sleep on a bed with a hard mattress.
- Engaging in long sitting activities (driving, working on the computer), it is necessary to change the posture from time to time, and organize rest and warm-up.
- When standing for a long time, lean on something.
- Do not wear high heels for two consecutive hours.
- Take time for moderate physical activity (swimming, fitness).
- Track your weight-excess weight may cause back pain.
- Try not to lift weights.
- Do not move suddenly and bend or bend over.
- Timely treatment of urological and gynecological diseases.
Annual preventive visits to the therapists will also be beneficial. It can eliminate the pathology detected early without waiting for the development of complications.






















